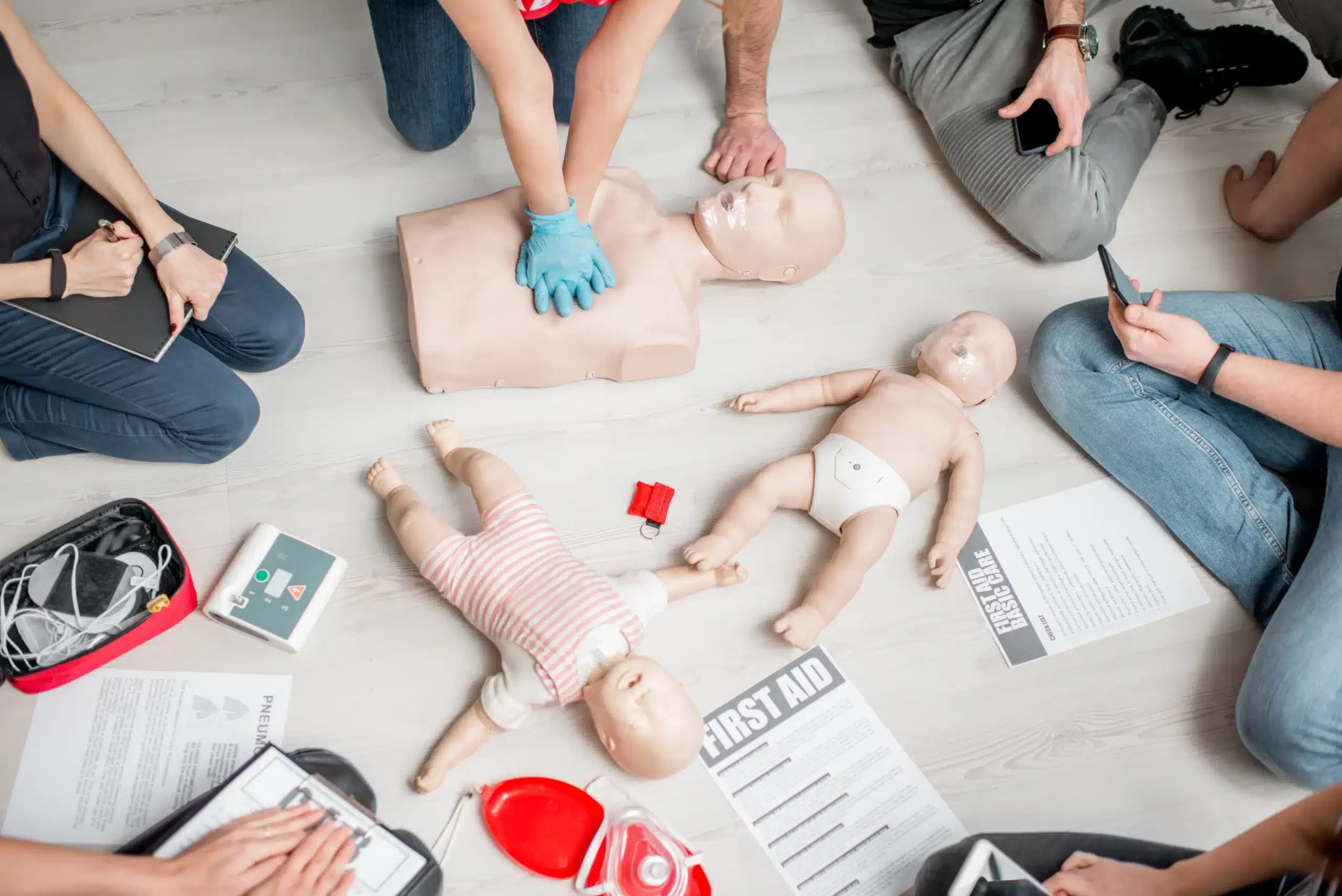
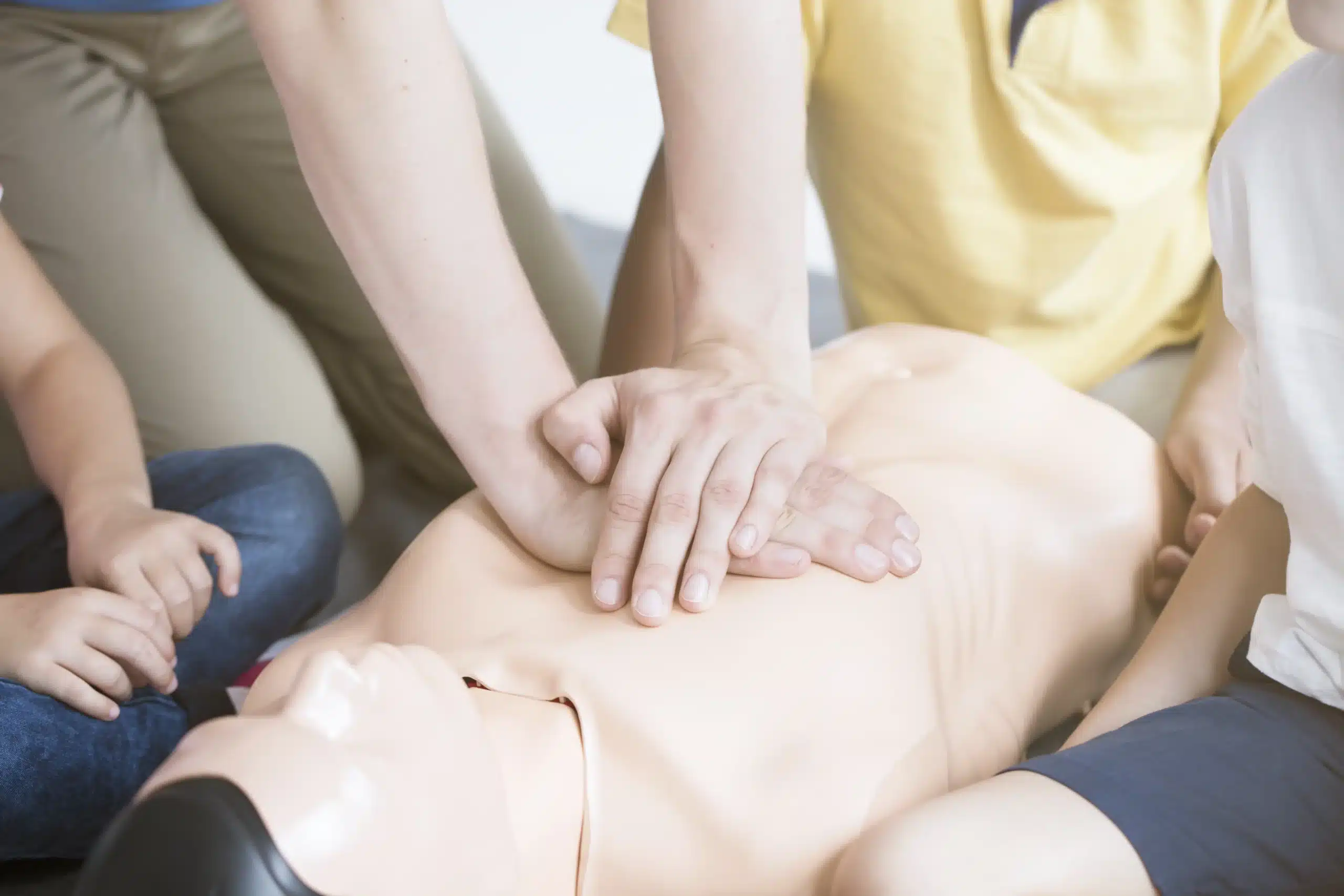
When seconds make the difference between life and death, CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) becomes the ultimate game-changer. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or an everyday individual, understanding and applying CPR could save a life. This guide will explore what CPR is, why it’s essential, its history, and how you can become proficient in this life-saving skill.
What Is CPR and Its Role in Healthcare?
The Definition of CPR
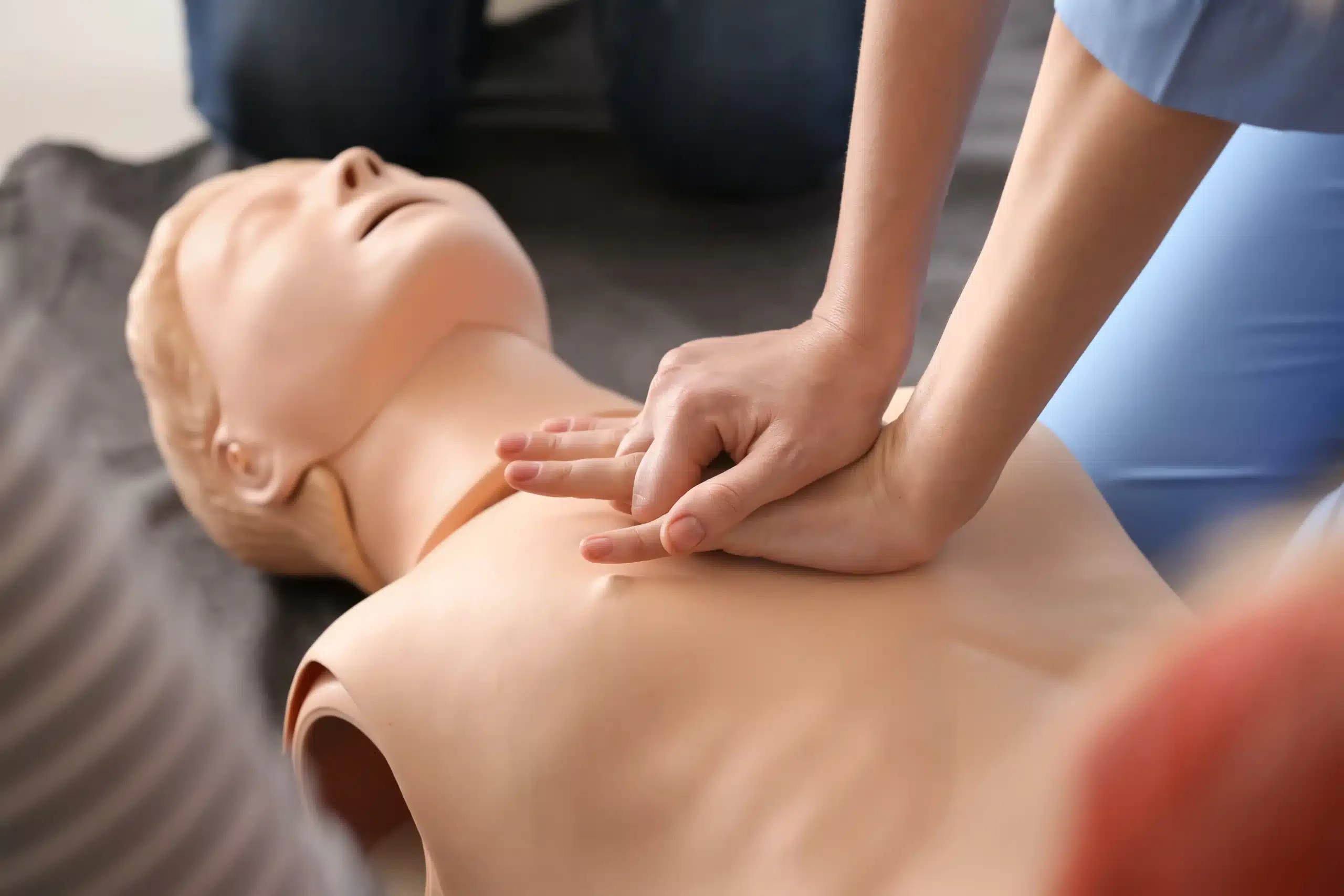
At its core, CPR combines chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood flow and oxygenation during cardiac or respiratory emergencies. This procedure keeps oxygen circulating to vital organs like the brain and heart, buying critical time until advanced medical care arrives.
How CPR Works
The process involves two key steps:
- Manual Chest Compressions – These mimic the heart’s pumping action, pushing blood through the body.
- Rescue Breaths – These provide oxygen to the lungs when the individual isn’t breathing on their own.
CPR is applicable in various settings, from hospitals to public spaces, and bridges the gap between an emergency and professional medical intervention. Without timely CPR, brain death can occur within four to six minutes of cardiac arrest.
The History of CPR
Early Foundations
The roots of CPR date back to the 18th century with basic chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. Fast forward to the 1950s, mouth-to-mouth resuscitation became a standardized technique. By the 1960s, the American Heart Association (AHA) formally introduced CPR guidelines, revolutionizing emergency care.
Key Milestones
- 1958: Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation gains medical acceptance.
- 1960s: CPR is standardized with chest compressions and rescue breaths.
- 2000s-onward: Continuous research refines methods, making CPR more effective.
Today, CPR integrates science-backed techniques that apply to both the medical community and the public.
The Life-Saving Importance of CPR
Hard-Hitting Statistics
The statistics from AHA are startling:
- About 350,000 cardiac arrests occur outside hospitals in the U.S. annually.
- 70% of these cases happen at home, highlighting the need for public CPR knowledge.
- Providing bystander CPR can double or triple survival rates in cardiac emergencies.
The “Chain of Survival”
CPR plays a crucial role in what’s called the chain of survival—a sequence of actions that maximize a person’s chance of surviving cardiac arrest. The sequence includes:
- Early recognition of the emergency.
- Immediate CPR.
- Rapid defibrillation.
- Advanced life support.
Why Bystander Intervention Matters
When someone collapses due to cardiac arrest, every second counts. Immediate CPR maintains circulation until professional responders arrive. Communities that prioritize CPR training see significantly higher survival rates from cardiac arrest.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in CPR
Healthcare Professionals as First Responders
For healthcare workers, CPR proficiency isn’t optional—it’s mandatory. Whether you’re a nurse, paramedic, or hospital administrator, the ability to perform effective CPR is a core requirement. Professionals often encounter cardiac emergencies, whether in hospitals, outpatient settings, or community spaces.
Ongoing CPR Training Is Essential
CPR techniques evolve based on science and research. Regular training and recertification ensure healthcare professionals are equipped with the latest protocols, such as compression-only CPR and updated compression-to-breaths ratios.
Key Groups Needing Training
- Nurses and Physicians – Frequently respond to emergencies as part of hospital code teams.
- Paramedics and EMTs – Provide pre-hospital life support.
- Hospital Administrators – Might coordinate staff training and disaster preparedness.
CPR Training and Certification
How to Get Certified
To become CPR certified, you can enroll in courses like those provided by the American Heart Association (AHA). Training typically lasts a few hours and equips you with hands-on experience to perform CPR confidently.
Key Certification Options:
- CPR & First Aid – For general emergencies.
- Basic Life Support (BLS) – Specialized for healthcare professionals.
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) – Focused on advanced techniques.
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) – For pediatric emergencies.
Where to Train?
Check out Safety Training Seminars, which provide AHA-certified courses tailored to various professional needs.
Empowering the General Public
While healthcare workers are always on the frontlines, CPR training isn’t exclusive to them. Teaching CPR to the general public, especially in schools and workplaces, equips communities to handle emergencies effectively.
Debunking Myths About CPR
Some of the myths surrounding CPR include:
“Only Trained Professionals Should Perform CPR”
This myth deters people from helping when every second matters. Reminder: imperfect CPR is better than no CPR.
“CPR Can Hurt the Patient”
While it’s true that chest compressions might cause fractures, the potential to save a life far outweighs the risk.
“It’s Hard to Learn CPR”
Modern CPR courses are straightforward, combining in-person practice with online learning modules.
Key Takeaways
- CPR saves lives. Its role in the chain of survival makes it vital for cardiac or respiratory emergencies.
- Both healthcare professionals and the public benefit from CPR training. Proficiency in CPR doubles or even triples survival chances in emergencies.
- Certification is accessible and equips anyone—from medical staff to everyday heroes—with skills to act decisively.
Empower Yourself Today
Are you ready to be someone’s lifeline? Consider CPR certification through trusted providers like Safety Training Seminars. Their American Heart Association-certified courses prepare you to save lives, whether in a professional or personal setting. Start your life-saving journey today.